 “Today, we’re asking “How many national libraries are there in the United States?”
“Today, we’re asking “How many national libraries are there in the United States?”
For most countries, the answer is usually one.
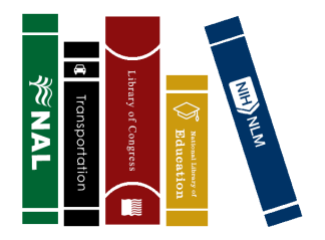
But the United States actually has five.
In addition to the National Library of Medicine, the other national libraries are the Library of Congress, the National Agricultural Library, the National Library of Education, and the National Transportation Library.
National libraries or libraries established by the government of a country serve as preeminent repositories of information. Often, they include numerous rare, valuable, or significant works and play an important role in the preservation of their countries’ cultures and intellectual traditions.
National libraries are commonly open to the public for research, and while members of the public may not directly check out items, they may be able to obtain them through interlibrary loan. National libraries are also increasingly making their collections available online, as copyright and digitization projects allow.”
Source: NLM Announcements from the NLM Office of Communications, July 25, 2018.
You must be logged in to post a comment.